

Metal heat treatment is a process of heating the metal workpiece in a certain medium to an appropriate temperature, and then cooling it at different speeds after keeping it at this temperature for a certain time.
Metal heat treatment is one of the important processes in mechanical manufacturing, compared with other processing processes, heat treatment generally does not change the shape of the workpiece and the overall chemical composition, but by changing the internal microstructure of the workpiece, or changing the chemical composition of the surface of the workpiece, endowing or improving the performance of the workpiece. It is characterized by improving the intrinsic quality of the workpiece, which is generally not visible to the naked eye.
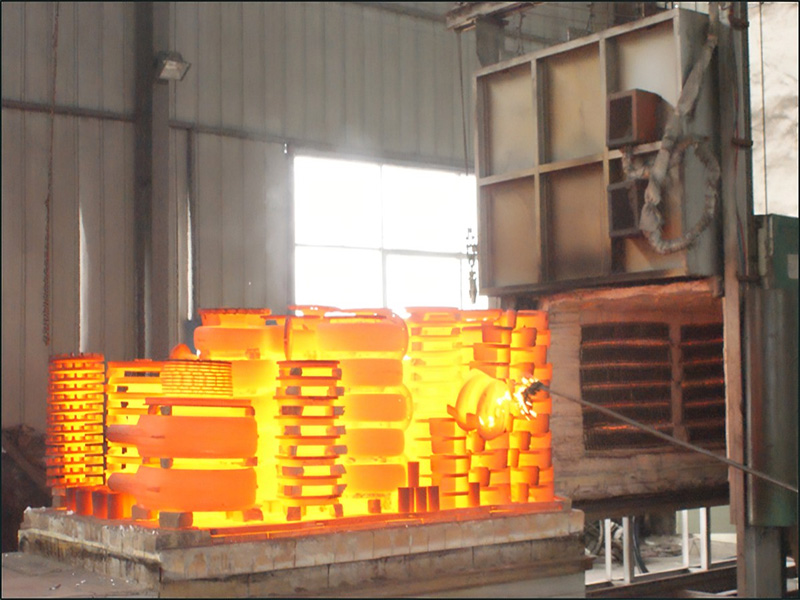
In order to make the metal workpiece have the required mechanical properties, physical properties and chemical properties, in addition to rational selection of materials and various forming processes, heat treatment process is often essential. Iron and steel is the most widely used material in the machinery industry. The complex microstructure of iron and steel can be controlled by heat treatment, so the heat treatment of steel is the main content of metal heat treatment. In addition, aluminum, copper, magnesium, titanium and their alloys can also change their mechanical, physical and chemical properties through heat treatment, in order to obtain different performance.
In the process from Stone Age to Bronze Age and Iron Age, the role of heat treatment is gradually recognized. As early as 770 BC to 222 BC, the Chinese had discovered in production practice that the properties of copper and iron would change due to the influence of temperature and pressure deformation. The softening treatment of white cast iron is an important process for manufacturing agricultural tools.
In the sixth century BC, steel weapons were gradually adopted. In order to improve the hardness of steel, quenching technology was developed rapidly. Two swords and a halberd unearthed from Yanxidu, Yixian County, Hebei Province, China, have martensite in their microstructure, indicating that they have been hardened.

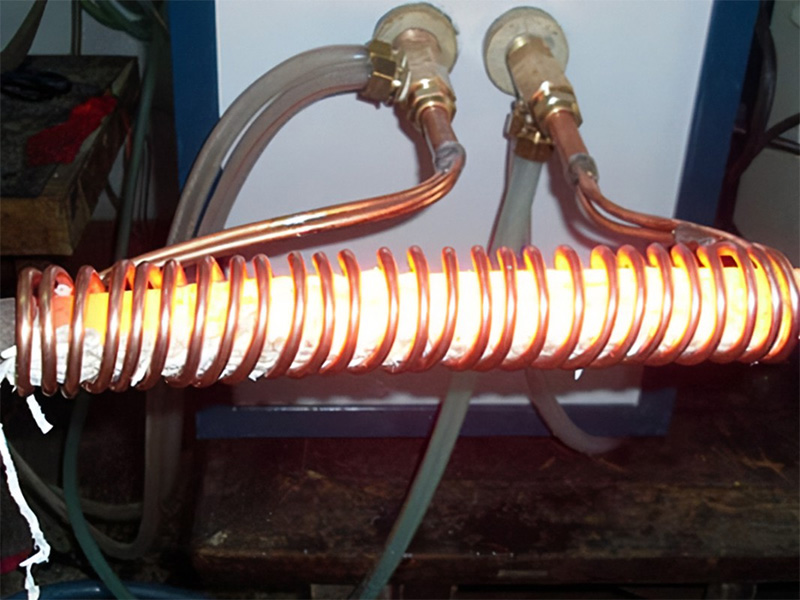
With the development of quenching technology, people gradually discover the influence of refrigerant on quenching quality. Pu Yuan, a man of Shu of The Three Kingdoms, once made 3,000 dao for Zhuge Liang in the xigu valley of today’s Shaanxi Province. According to legend, he sent his people to Chengdu to get water for quenching. This shows that in ancient times China paid attention to the cooling capacity of different water qualities, as well as the cooling capacity of oil and urine. A sword unearthed in China from the tomb of King Jingwang of Zhongshan in the Western Han Dynasty (206 BC ~ AD 24) contains 0.15-0.4% carbon in the heart, but more than 0.6% carbon in the surface, indicating that carburizing process has been applied. But at that time as a personal “craft” secret, refused to spread, so the development of slow.
In 1863, British metallographers and geologists showed six different metallographic structures of steel under the microscope, proving that when steel is heated and cooled, the internal structure changes, and the phase at high temperature in steel changes into a harder phase at rapid cooling. The theory of iron isomerism established by Osmond, a Frenchman, and the diagram of iron carbon phase formulated by Austin, an Englishman, laid a preliminary theoretical foundation for modern heat treatment technology. At the same time, people also studied the metal protection methods in the heating process of metal heat treatment, in order to avoid the metal oxidation and decarbonization in the heating process.

From 1850 to 1880, there were a series of patents for the application of various gases (such as hydrogen, gas, carbon monoxide, etc.) for protective heating. In 1889 ~ 1890 the British Lake obtained a variety of metal bright heat treatment patent.
Since the 20th century, the development of metal physics and the transplantation and application of other new technologies have made the metal heat treatment process develop further. A remarkable progress was the application of rotary furnace to carburizing gas in industrial production from 1901 to 1925. In the 1930s, the dew point potential difference meter appeared, so that the carbon potential in the furnace atmosphere can be controlled. Later, the method of further controlling the carbon potential in the furnace atmosphere by using carbon dioxide infrared instrument and oxygen probe was studied. In the 1960s, the heat treatment technology used the role of plasma field, the development of ion nitriding, carburizing process; With the application of laser and electron beam technology, new surface heat treatment and chemical heat treatment methods have been obtained.

For Further Details,Please Feel Free To Contact Us: